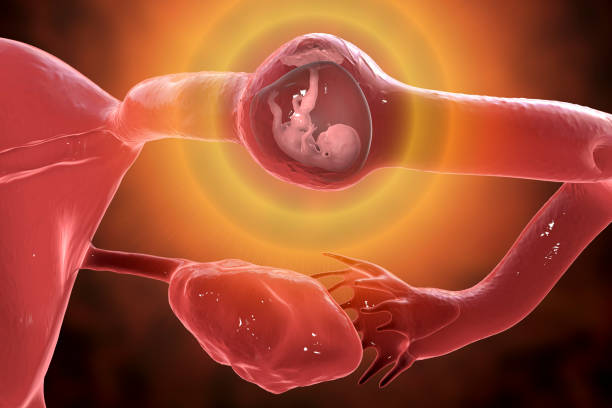
what is ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy refers to the condition in which a normally fertilised ovum implants outside the usual uterine cavity.
Most people mistakenly believe that ectopic pregnancies only happen when the fertilised ovum implants in the fallopian tubes, but this is incorrect. About 98 percent of ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tubes, during which time it is known as a tubal pregnancy. However, the fertilised ovum can also implant in about 0.2 percent of cases in both ovaries (ovarian pregnancy), in the cervix (cervical pregnancy)
Any female of reproductive age who exhibits early onset amenorrhea, abdominal pain, and vaginal bleeding should be evaluated for ectopic pregnancy. This includes ruling out other conditions such as abortion, acute salpingitis, acute appendicitis, haemorrhage in the corpus luteum cyst, cystitis, and finally complicated fibroid or ovarian cyst.
It is impossible to determine the distinction between tubal and non-tubal ectopic pregnancy from a simple history; instead, this must be demonstrated through an ultrasound investigation.
Any woman who experiences early onset amenorrhea, abdominal pain, or bleeding should see a doctor to rule out an ectopic pregnancy because this is the most deadly complication of ectopic pregnancy. If this happens, the patient may go into shock and eventually pass away.
Pregnancy and ectopic pregnancy
Getting pregnant after an ectopic pregnancy depends on a number of factors. First, if the patient is diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy and it is discovered early, the pregnancy sac may be removed without removing any parts of the female genital system. Additionally, some medication, such as mexothrate, may be used in place of surgery to allow for the absorption of some conceptions without harming the female genital system. However, if it is discovered late or even when the patient is already.
Another factor is that having an ectopic pregnancy, whether it be the first time or a subsequent one, lowers the likelihood of becoming pregnant. Additionally, using an intrauterine device (IUD) increases the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy, which lowers the likelihood of a uterine pregnancy in general. If this is the case, switching to another method of contraception is advised.
NOTE: This article only for information. Firstly you should visit your family doctor